Description of the Pilot
What is the data challenge of the pilot?
Soil process data, like data from rainfall simulation experiments for erosion studies combine several aspects of common hindrance for FAIR data in earth system sciences. Despite them being of central importance to develop mitigation strategies against soil degradation, such experiments are very specific to the needs and tools of the respective working groups. The data exisit in various formats and often lack proper description, clear metadata and common standards. To make this data FAIR without forcing the different groups to abandon their specific procedures is the central challenge of our NFDI4Earth pilot.
What will be the key achievements of the pilot?
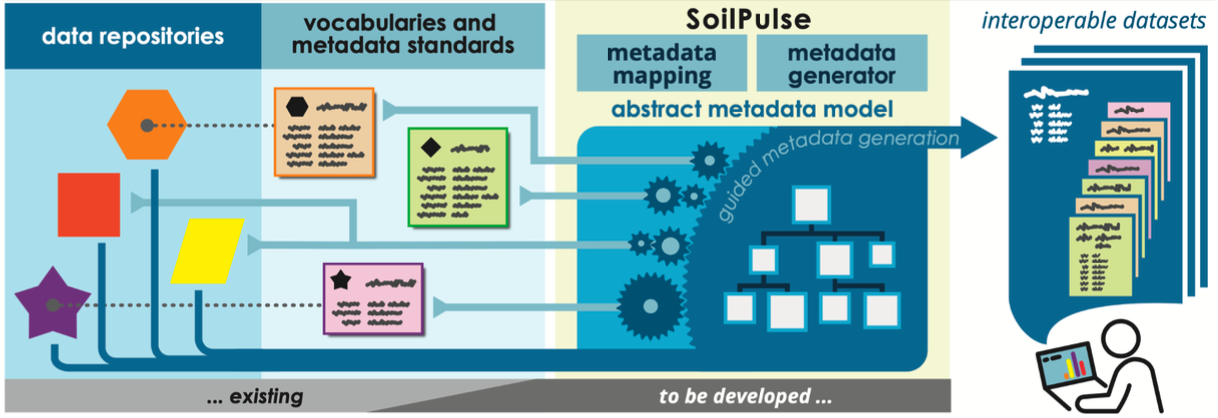
We are advancing the established BONARES metadata standard through and an adapated scheme, which is capable for soil erosion process measurements. To make it easy to adhere existing data and established procedures to this scheme, we develop a Python package for guided, semiautomatic with wrapping of given files to ensure that their contents will be understandable for both humans and machines. We aim to harvest as many metadata as possible from the provided files and to generate mapping procedures which can be applied to further data of the same structure. Through this we seek to provide an easy tool for FAIR data preparation. Moreover, we are building quality controlling data processing features. Once the data is understood by the machine, standard evaluations and visualisations will be performed as interactive control. Interoperability and reusability of the data will be demonstrated with automated tests, which implies that datasets can be standardized linked to earth system models.
What is the technological backbone you rely upon?
SoilPulse assists metadata generation and API-assisted upload for new and existing datasets through an open Python-package and with a streamlit-driven web app frontend, strongly extending current MetaEditors. It will be publicly documented and hosted on GitHub. To improve findability of interoperable SoilPulse datasets, they will be listed by DOIs in the GitHub repo. A metadata-tag in the dataset linking to SoilPulse is foreseen. Defined FAIR MI tests and the automatic generation of human-readable reports will test data set interoperability and reusability.
Which are the standards and interoperability approaches used in the pilot’s context?
The semantically interoperable SoilPulse metadata standard will build upon existing standards (e.g. BONARES; ISCN, building on INSPIRE and Dublin Core), vocabularies (e.g. AGROVOC, upcoming GAIA Data GO FAIR) and data harmonization approaches (e.g. SoDaH; ESIP).
Which improvements are made compared to the status quo?
Interoperability of data repositories will be ensured by mapping their individual data structures to common vocabulary and metadata standards. Automated reusability tests will be developed. Data curation effort for individual researchers will be reduced through guided metadata generation and the ability to retain their established data structure and workflows.